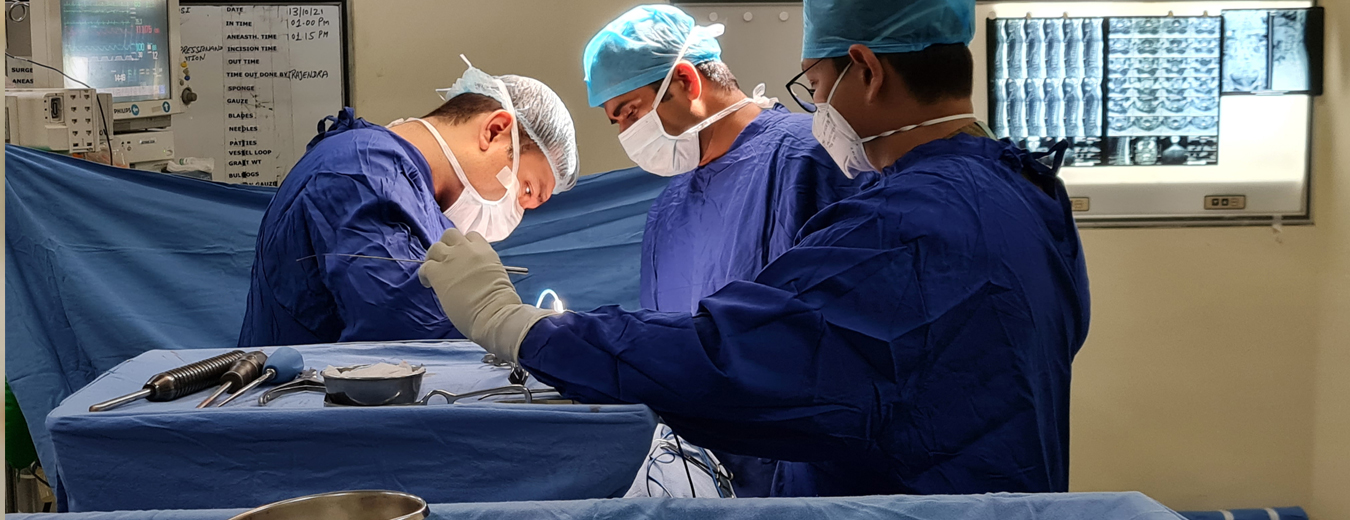
Microendoscopic disectomy
It is a minimally invasive procedure performed through a tubular device and designed to relieve pain caused by herniated disc pressing on nerve roots. It is performed by technologically advanced and newer instruments to remove the prolapsed disc with very small incision, decrease dissection and decreased disruption of normal tissue. An incision of size 5 mm is made over the site of disc.
Because the incision is so small, there is negligible surgical trauma to normal tissue and muscles, negligible blood loss. Special retractors are placed in the incision. An endoscope, which is basically a tube with camera at the tip is placed inside the incision and we reach to the spine. Small amount of bone is removed and herniated disc is removed through that hole. Free nerve root is visualised through the endoscope.
Then endoscope and retractors are removed. Since the incision is so small some surgeon choose to put band aid over the wound. Usually the scar of surgery is not noticeable after a month time.
This can also be done by a small key hole incision – Endoscopic Discectomy In more severe cases, your doctor may replace the disc with an artificial one or remove the disc and fuse your vertebrae together. This procedure, along with a laminectomy and spinal fusion, adds stability to your spinal column.